Frequently asked questions
General
What is high throughput screening (HTS)?
High throughput screening is a method for rapidly quantifying cellular response to perturbation (typically, the application of one or more drugs). Microtiter plates with multiple wells can have different combinations of drugs, drug doses, and cell lines in each well, thus having the potential to generate large amounts of data.
What is the drug-induced proliferation rate (DIP rate)?
The DIP rate is defined as the steady-state rate of proliferation of a cell population in the presence of a given concentration of drug. It is easily quantified as the slope of the line on a plot of the doubling of cell populations versus time. For further information, see Harris et al. Nature Methods 2017.
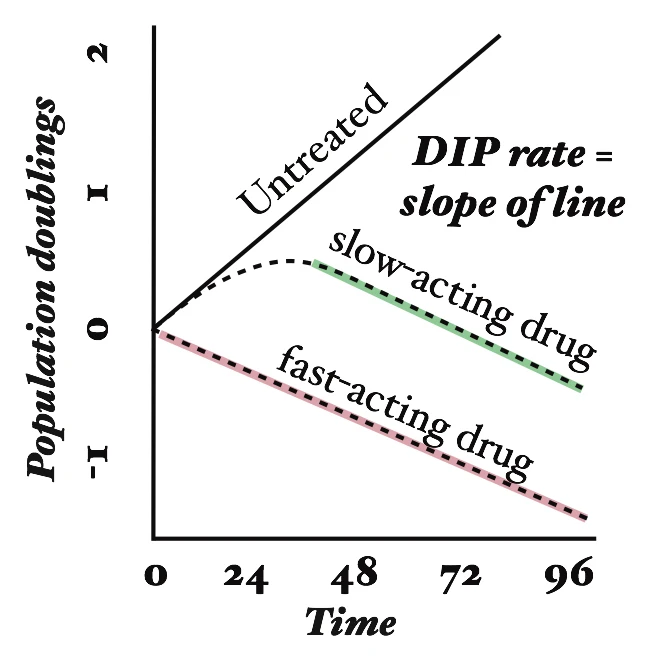 Image: Hypothetical growth curves (in log scale) for a cell line untreated and treated with two different drugs. Also shown is drug-induced proliferation (DIP) rate, defined as the slope of the line after the drug effect has stabilized. Figure from Harris et al. Nature Methods 2017.
Image: Hypothetical growth curves (in log scale) for a cell line untreated and treated with two different drugs. Also shown is drug-induced proliferation (DIP) rate, defined as the slope of the line after the drug effect has stabilized. Figure from Harris et al. Nature Methods 2017.
What are the advantages of the DIP rate over end-point viability?
Traditionally, dose response curves were constructed by measuring cell counts at a single time point after drug application (e.g. 72 hours). Metrics such as IC50 were then calculated against this curve.
Dose response curves using traditional metrics of drug effect can result in erroneous and misleading values of drug activity parameters, skewing data interpretation. This is because these metrics suffer from time-dependent bias (the metric value varies with the time point chosen for experimental measurement), arising from (i) exponential growth and (ii) delays in drug effect stabilization. For more information, see Harris et al. Nature Methods 2017.
My question isn't answered here. Where can I get help?
If the answer to your question isn't available in this FAQ or elsewhere in this manual, please contact us via our chat room.
Installation
Why am I seeing "Bad Request (400)" when I try to access Thunor Web after installation?
Please check that the value for DJANGO_HOSTNAME set in thunor-app.env matches the
hostname used in your browser. After changing the value, you'll need to restart
Thunor Web: python thunorctl.py restart.
How do I log in?
Use the account you created during installation. If you didn't create an account,
run python thunorctl.py createsuperuser.
How do I customize my Thunor Web installation?
See the list of configuration options. Remember to
restart Thunor Web after making changes, by running python thunorctl.py restart.
How do I use an external Postgres database server?
Set the POSTGRES_HOST, POSTGRES_USER and POSTGRES_PASSWORD environment variables
with the connection details of your Postgres server. Initialize the database with
python thunorctl.py migrate.